Of all the many problems that can afflict the back and spine, upper back pain is definitely not the most common. The individuals who suffer from it know that it can be just as painful as other back issues! Upper back pain can be either acute or chronic, and it’s often significant enough to have a dramatic negative impact on sufferers’ quality of life. Upper back pain is generally used as a catchall term describing any sort of back pain that affects the shoulders, ribs, mid-back, and chest.
What is Upper Back Pain?
Any sort of pain occurring from the middle of your up to and across your shoulders can be considered upper back pain. This area is medically known as the thoracic region, and it stretches all the way from the lower back to the neck. The vertebrae of the spine here connect to many muscles in the back as well as the ribs. Many individuals experience upper back pain at some point in their lives. Though it’s less common than lower back pain, it can be every bit as excruciating as that more frequently-felt issue. Upper back pain can make a significant negative impact on your quality of life.
Symptoms of Upper Back Pain
Common symptoms of this condition include:
- Muscle spasms (feeling of tightness or “knots”)
- Pain accompanying deep breaths
- Pain with shoulder or neck motion
- Pain on contact with your back
- Pain when you shift your back
12 Causes of Upper Back Pain
There are many symptoms that can be felt by those who suffer from upper back pain. Most people who suffer this pain are not aware of the number of factors that can act to cause upper back complications. The contributors to upper back pain can be any one or more of the reasons that lead to this discomfort.
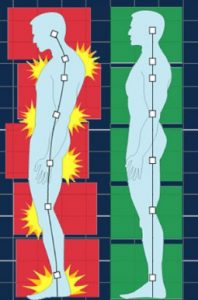
Poor Posture
This is one of the major reasons that can cause upper back pain and is common among people who work for long hours on computers while sitting at a desk with hunched shoulders. Repeatedly looking down while texting on a cell phone can also lead to upper back pain. Mothers who are breastfeeding can get such pain because of the way they hold their child. It is important, for avoiding back pain, that you correctly align your head through your body, as if it juts forward, it has a weight that causes a strain on the upper back muscles and neck, and this can lead to their weakening and becoming overstretched.
Muscle Strain
This can occur if you do not use the right technique while lifting objects. Bend at the knees if you have to lift things, and ensure that the heavy object you are carrying is close to the body, as this will reduce the strain on the back muscles which can often lead to pain.
Trauma/Injury
When you are involved in car accidents or other traumatic events, this can lead to back pain for a number of reasons. A spinal bone or vertebra can be fractured. The vertebra can also be displaced and press on the spinal nerve, and this can lead to pain.
Vertebral Compression Fractures
This problem commonly occurs in the elderly due to osteoporosis that results in the thinning of the bones. Fractures can also occur in the upper spine from falls, but where the osteoporosis is severe these fractures can even result from sneezing or coughing and can lead to a dowager’s hump, a hunched posture that then causes back pain.
Herniated Spinal Disk
When intervertebral disc bulge or herniate and move out of position this can lead to upper back pain that is chronic. These discs are tissue rings that are positioned between each vertebra. Their function is to provide spinal support and to act as shock absorbers. They have an inner layer that is spongy and an outer layer that is tough. If the outer layer deteriorates, the inner layer will protrude outwards. This results in inflammation and irritation of the spinal nerves that are close by and this can result in a chronic condition of upper back pain.
Myofascial Pain
The fascia is the connective tissue between muscles and this can be affected. Patients who suffer from myofascial pain will have knotted points that trigger pain when they are pressed, and the pain also has a sensation of tingling and burning.
Spondylosis
This is an arthritic form of pain that can affect the neck and both the upper and lower back. Bone spurs develop and these act to narrow the channel that contains the spinal chord. Spinal nerves can get pinched and this can lead to a feeling of numbness and weakness in the legs that can have an effect on normal walking.
Carrying Heavy Backpacks
This is an upper back injury that kids who carry heavy backpacks can suffer from. Backpacks that are very heavily loaded are not good for the spine, and this problem can also come about from not carrying the backpack correctly, with both the support straps.
Infection
An abscess that is spinal epidural or paraspinal can lead to a compression of the spinal nerves or spinal chord in the thoracic region, and this can lead to pain besides other symptoms.
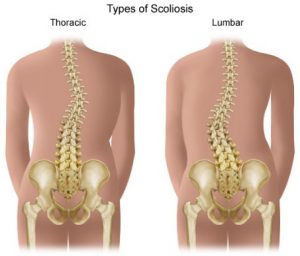
Scoliosis
This is a condition that comes from curves in the spine or a curve that is unusual. Your spine will look like the letter S or C when seen from the back. The spine curving to the left or right in the thoracic region or the upper back leads to pain. The curve can affect soft tissues, muscles, and the spinal nerves.
Problematic Kyphosis
A side view of the sine should have it curving outward in the thoracic region or upper back and this is known as the kyphotic curve. If this curve is pronounced then this leads to problematic kyphosis. Osteoporosis, as well as other conditions, can also lead to problematic kyphosis that affects the thoracic spine and leads to pain in the upper back.
Other Conditions
There are also a number of medical conditions that can lead to pain in the upper back.
- GERD or Acid Reflux
- Angina or other cardiac conditions
- Thoracic nerve damage
- Cancers of the thoracic spine or cavity
Diagnosing Upper Back Pain
Your doctor should begin by interviewing you to collect information about your current state of health, your work, and the full range of physical activities you engage in. The next step is a physical examination. This is sometimes followed by an imaging test (e.g. an X-ray or MRI) to look for causes like herniated discs or bone fractures that could be causing your pain. Depending on the results of your initial examinations, further tests may be required.
Treatments For Upper Back Pain
Medication
The pharmacological solution to upper back pain starts with common oral pain medication. Examples include Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen, Naproxen, and some forms of anticonvulsants. While these medications are sometimes effective, there are also potential side effects to worry about, including addiction and organ damage.
Epidural Steroids
In cases where oral medications don’t resolve an upper back pain problem, epidural corticosteroid injections may be the answer. These are anti-inflammatory compounds that are effective on a wider variety of body tissues. They’re frequently used to treat conditions like arthritis. When administered via injection, corticosteroids for back pain are frequently combined with a local anesthetic like lidocaine. This numbs the affected tissue and further reduces the amount of pain.
Facet Joint Injections
Steroids can also be injected into the facet joint if a doctor identifies this as the source of an upper back pain issue. Medial branch blocks may also be employed to bring pain relief. Injection procedures like this do carry risks of side effects.
Discectomy
If your doctor determines that your upper back pain is being caused by a herniated disc, he or she may call for a discectomy. This is a rare but effective way to resolve a specific back pain issue, and the treatment involves minimal invasiveness. Surgeons will remove either an entire disc or the herniated portion. Percutaneous disc decompression is another term for this type of procedure. A proper discectomy can provide pain relief for up to two years. There are potential side effects to worry about including infections, nerve damage, and bleeding.
Vertebroplasty / Kyphoplasty
If your pain is coming from a spinal fracture, vertebroplasty may be the answer. This procedure involves anesthetizing the affected area and inserting acrylic cement to seal the fractured vertebra. Kyphoplasty is a similar procedure that also involves inserting a small balloon to lend additional support.
Doctors treating upper back pain may prescribe medications for oral use or recommend trigger point injections for muscle spasms. In the long term, physical therapy is often recommended to maintain and improve mobility and flexibility. Your doctor may also suggest forms of treatment like chiropractic care or acupuncture.
Home Remedies for Upper Back Pain
Upper back pain is not usually a critical problem though it can be inconvenient and uncomfortable. Severe pain arising suddenly (e.g. after an injury) or growing worse over time is a cause for concern, and you should always seek professional health care when required.
You may find relief from intermittent upper back pain with the following home treatments:
Rest
Taking a break is always a good idea when your back is in pain. Don’t spend too much time out of action; protect yourself from further injury by slowly building up to your former level of activity.
Over-The-Counter Medication
As noted above, oral pain medications can often help with upper back pain. Acetaminophen (i.e. Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories (e.g. aspirin, Motrin, Aleve, Advil, etc.) can reduce the amount of pain and swelling you experience. Remember to check medication labels carefully and use them as directed by the manufacturer.
Icing
You can use a commercially-prepared cold pack to treat back pain or make your own. Simply fill a closed plastic bag with ice and wrap it in a towel. Apply cold to affected areas for no more than 20 minutes every two to three hours and repeat this as necessary during the first three days.
Heat
Heat therapy should only be started after 72 hours have passed. Apply moist heat and then stretch gently to relieve stiffness and improve your mobility.
Exercise
Strengthening the muscles in your back, stomach, and shoulders is an excellent long-term solution to improve your posture, reduce pain, and decrease the chances of injury in the future.
Better Posture
Stand up straight and sit tall. Slumping and slouching are not good for an injured back. Adjust your working environment as necessary to ensure that it’s ergonomic.
Good Suppor
Check your shoes and mattress to make sure you’re being properly supported in both your waking and sleeping hours.
Reduce Stress
Try relaxation exercises, deep breathing exercises, and meditation in order to manage your stress levels better.
When to See a Doctor?
Consult a doctor immediately if you experience back pain in combination with any of the following symptoms:
- High fever
- Unexplained weight loss
- Chest pain
- Loss of bowel or bladder control
- Inability to urinate
- Swelling or deformity
- Pain linked to an accident
- Constant pain that gets worse overnight
How Can I Help Prevent Upper Back Pain?
- When lifting heavy weights, avoid twisting your torso if at all possible.
- Getting regular exercise is the best way to avoid back pain. Swimming or walking are excellent, as are guided forms of stretching exercise like yoga or Pilates.
- Sit ergonomically. When working at a desk, your feet should be flat on the floor, knees directly above them, and your lower back should be supported. Type with straight wrists.
- Take breaks frequently to keep your upper body from getting tense. Simple desk exercises like shoulder shrugs or shoulder squeezes can do a great deal to prevent upper back pain.